Automotive fasteners: everything you need to know to choose a supplier
Automotive fasteners are not just a matter of small parts: they are a technical universe that directly impacts the safety, efficiency and quality of every vehicle. Understanding how it is manufactured, what characteristics it must meet and how to choose the right supplier is essential for any professional operating in this industry. This article is designed by LEMEC to accurately answer those key questions.
What is automotive fasteners and why is it so critical in the industry?
Automotive fasteners include all fasteners, such as screws, bolts, rivets and studs, used to assemble and secure the various components of a vehicle. Although they often go unnoticed, these elements fulfill essential structural and safety functions. In fact, a failure in the fasteners can seriously compromise the mechanical integrity of the car.
In the automotive industry, fasteners must meet requirements for tensile strength, toughness, fatigue strength and tight tolerances. Its selection depends on the application, the type of materials it connects, the thermal environment and the vibrations it must withstand.
Need help?
Contact our technical office and tell us about your project.
We will study your case and propose a solution to manufacture them.
How automotive fasteners are made: the cold heading process
Behind every screw is a high-precision industrial process. In the automotive industry, the most commonly used manufacturing method is cold heading, a technique that allows millions of parts to be produced with high precision and efficiency.
What is cold heading in fasteners?
In the context of automotive fasteners, cold heading is the benchmark process for manufacturing technically demanding fasteners. Thanks to this technique, high-volume production is achieved while maintaining the dimensional quality, structural strength and mechanical performance required by the automotive industry.
Cold heading, also called cold forging, consists of plastically deforming a metal wire without applying heat, using high-power presses and specialized dies. This makes it possible to preserve the properties of the material and, in fact, to improve them thanks to strain hardening.
Advantages over other methods
This process has several advantages over traditional machining or casting:
- Low unit cost in large volumes.
- High production speed (up to hundreds of pieces per minute).
- Less material waste.
- Improved mechanical properties.
- Tight dimensional tolerances.
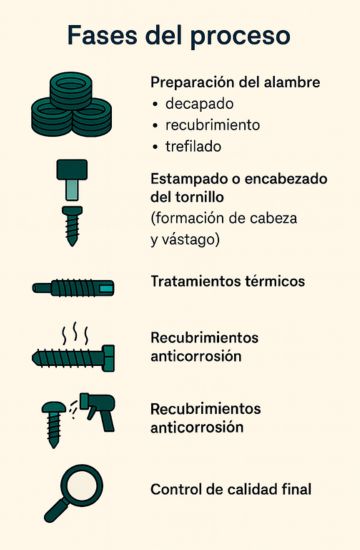
Phases of the process
The process includes:
- Wire preparation (pickling, coating, drawing).
- Stamping or heading of the screw (head and shank forming).
- Thread rolling.
- Heat treatments (quenching and tempering).
- Anti-corrosion coatings.
- Final quality control.
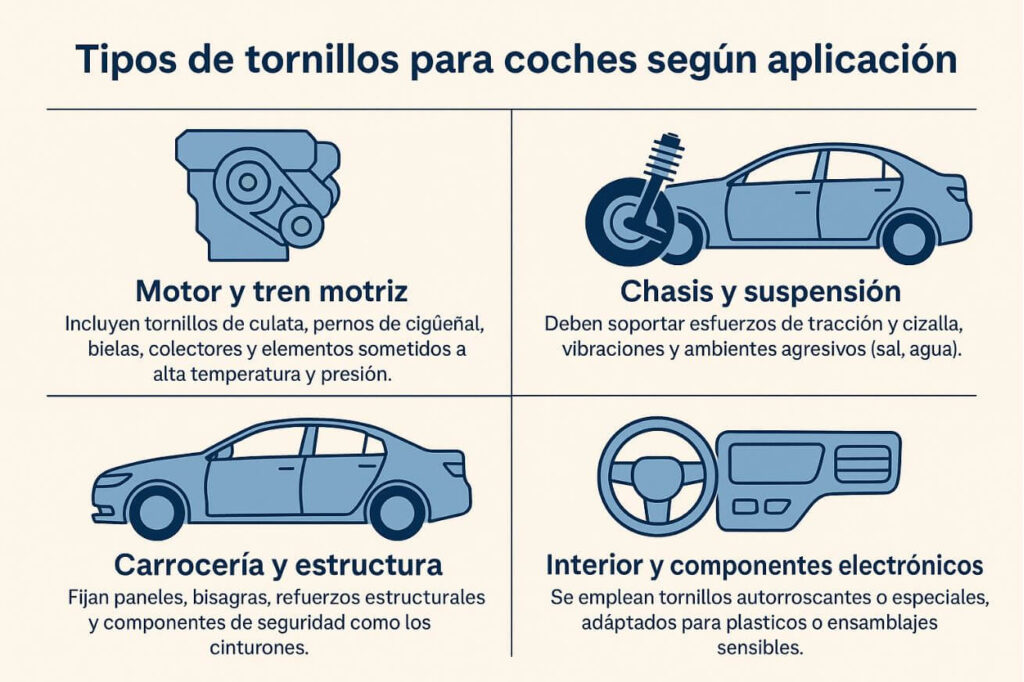
Types of car bolts by application
Different areas of the vehicle require different fastening properties. For this reason, fasteners are classified according to their location and function within the vehicle. The main types of fasteners used and their specific characteristics according to the area of application are listed below.
Engine and powertrain
In this critical area of the vehicle, the bolts are subjected to high temperatures, intense vibrations and extreme pressures. For this reason, high-performance bolts such as:
- Cylinder head bolts: designed to withstand intense thermal cycling and maintain engine sealing. They are usually class 10.9 or even torque-to-yield (TTY).
- Crankshaft bolts and connecting rods: require high tensile and fatigue strength, with a specific design to ensure integrity under dynamic loads.
- Exhaust and intake manifold fasteners: exposed to high temperatures, they require thermally stable coatings and rust-resistant materials.
Chassis and suspension
The chassis and suspension demand high tenacity bolts that resist dynamic loads, torsion and corrosive environments:
- Shock absorber bolts and suspension arms: subjected to constant bending and compression, they require alloy steel and weather-resistant coatings.
- Subframe and stabilizer bolts: structural safety elements that require absolute reliability.
- Brake fasteners: they must secure the caliper and disc under extreme stresses; fatigue tolerance is key here.
Body and structure
These bolts are used in both visible and internal joints of the vehicle monocoque:
- Fasteners for panels and structural reinforcements: combine moderate strength with light weight and corrosion protection.
- Hinge bolts and door/safety belt anchors: must meet impact and pull-out resistance standards.
- Modular assembly applications: where dimensional uniformity and surface treatment are essential to avoid noise or misalignment.
Interior and electronic components
The interior of the vehicle, although subject to fewer structural requirements, requires precision fasteners that do not damage that does not damage the assembled materials:
Screws with brake patches: ensure that they do not loosen due to vibration, essential in sensitive electronic modules.
Self-tapping or self-drilling screws: ideal for plastics or thin sheets, designed with geometries that minimize the risk of cracking.
Fasteners for displays, sensors, air conditioning: require low friction during tightening and electromagnetic compatibility.
Essential technical characteristics in automotive fasteners
To ensure safe and durable performance, automotive fasteners must meet stringent regulatory, metallurgical and finishing criteria.
International norms and standards
Standards such as ISO 898-1, DIN 933, SAE J429, among others, are applied. These regulate strength classes, materials, hardness and traceability.
Mechanical properties and heat treatments
Class 8.8, 10.9 or 12.9 bolts require treatments such as quenching and tempering to achieve adequate tensile strength and toughness.
Anti-corrosion coatings and finishes
The most common include electrolytic zinc plating, lamellar coatings (Geomet® type), passivation and special anti-corrosion treatments for demanding environments.
How to choose the ideal automotive fastener supplier
Choosing a reliable supplier is key to ensure the quality of the final product and the continuity of the supply chain.
Look for suppliers that offer:
- Complete traceability of the process.
- Quality certifications (ISO 9001, IATF 16949).
- Industrial production capacity.
- Automated quality control.
- Personalized technical advice.
- Commitment to sustainability.
Do you need fasteners for the automotive sector? What data to have ready before requesting a quotation
If you are going to request a quotation, prepare this information:
- Technical specifications: material, type, treatment.
- Dimensions and thread type.
- Technical drawing in case of customized fasteners.
- Specific application and environment of use.
- Estimated quantity and periodicity of the order.
- Packaging or technical cleanliness requirements.
A prepared supplier such as LEMEC will be able to help you define these variables.
Get in touch with us
Contact our technical office and tell us what kind of automotive fastener parts you need to manufacture.
We will study your case and propose a customized, fast and efficient cold stamping solution.